Introduction to Dementia and Assistive Technology
Dementia is a collective term for a range of neurological disorders that primarily affect memory, thinking, and behavior. This progressive condition can lead to significant impairments in daily functioning and can profoundly impact both patients and their caregivers. Various types of dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia, exhibit different symptoms, but they often share common challenges, including difficulty in communication, problem-solving, and maintaining independence. As dementia advances, individuals may struggle with tasks of daily living and experience changes in mood and personality, which highlights the need for effective support systems.
Assistive technology (AT) encompasses a diverse array of tools and devices designed to enhance the quality of life for individuals with disabilities, including dementia patients. The primary goal of assistive technology is to facilitate independence, ensuring that individuals can perform daily activities more effectively. This technology can range from simple tools, such as medication reminders and communication aids, to more advanced systems that incorporate smart home technology, tracking devices, and specialized software. By integrating assistive tech for dementia patients into their daily routines, individuals can retain a greater sense of autonomy and dignity.
The incorporation of assistive technology offers numerous benefits by promoting safety, improving communication, and enhancing overall well-being. For instance, memory aids can assist dementia patients in recalling important information, while monitoring devices can alert caregivers to changes in behavior or potential hazards. Additionally, AT can help foster social connections by enabling individuals with dementia to engage with loved ones, thereby combating the feelings of isolation that often accompany the condition. Hence, combining a deeper understanding of dementia with the appropriate assistive technology can significantly transform the day-to-day experiences of those affected and their families.
Types of Assistive Technologies for Dementia
Assistive technology plays a vital role in supporting dementia patients by enhancing their quality of life and facilitating daily living. Various categories of assistive technologies are specifically designed to help manage symptoms, encourage independence, and improve communication. These technologies can be broadly categorized into wearable devices, communication aids, memory aids, and smart home technologies.
Wearable devices include a range of tools designed to help monitor the health and safety of individuals with dementia. For example, GPS tracking devices can provide real-time location data, which is invaluable for caregivers in ensuring the safety of patients prone to wandering. Additionally, wearable health monitoring systems can track vital signs, alerting caregivers to any concerning changes. Such devices empower dementia patients by allowing them to maintain more autonomy while reassurance is provided to their families.
Communication aids are essential for individuals experiencing difficulties in verbal communication. Solutions such as speech-generating devices and applications enable dementia patients to express their needs and feelings more effectively. Furthermore, simple picture boards can facilitate communication by allowing patients to point to images or phrases, bridging the gap between them and their caregivers or loved ones, enhancing social interaction.
Memory aids are crucial tools for assisting patients in recalling important information and everyday tasks. Digital calendars and reminder apps can help patients keep track of appointments and medications. Similarly, electronic devices with pre-programmed messages can serve a dual purpose, offering cognitive stimulation while also providing gentle reminders for daily tasks.
Finally, smart home technologies are revolutionizing the living environments of dementia patients. Devices such as smart speakers can help control home systems and provide audible reminders or prompts. Smart lighting systems can aid navigation during night hours, enhancing safety and promoting independence. By integrating these assistive technologies into the daily lives of dementia patients, caregivers can significantly improve their emotional well-being and functional capabilities.
Wearable Devices: Monitoring and Safety
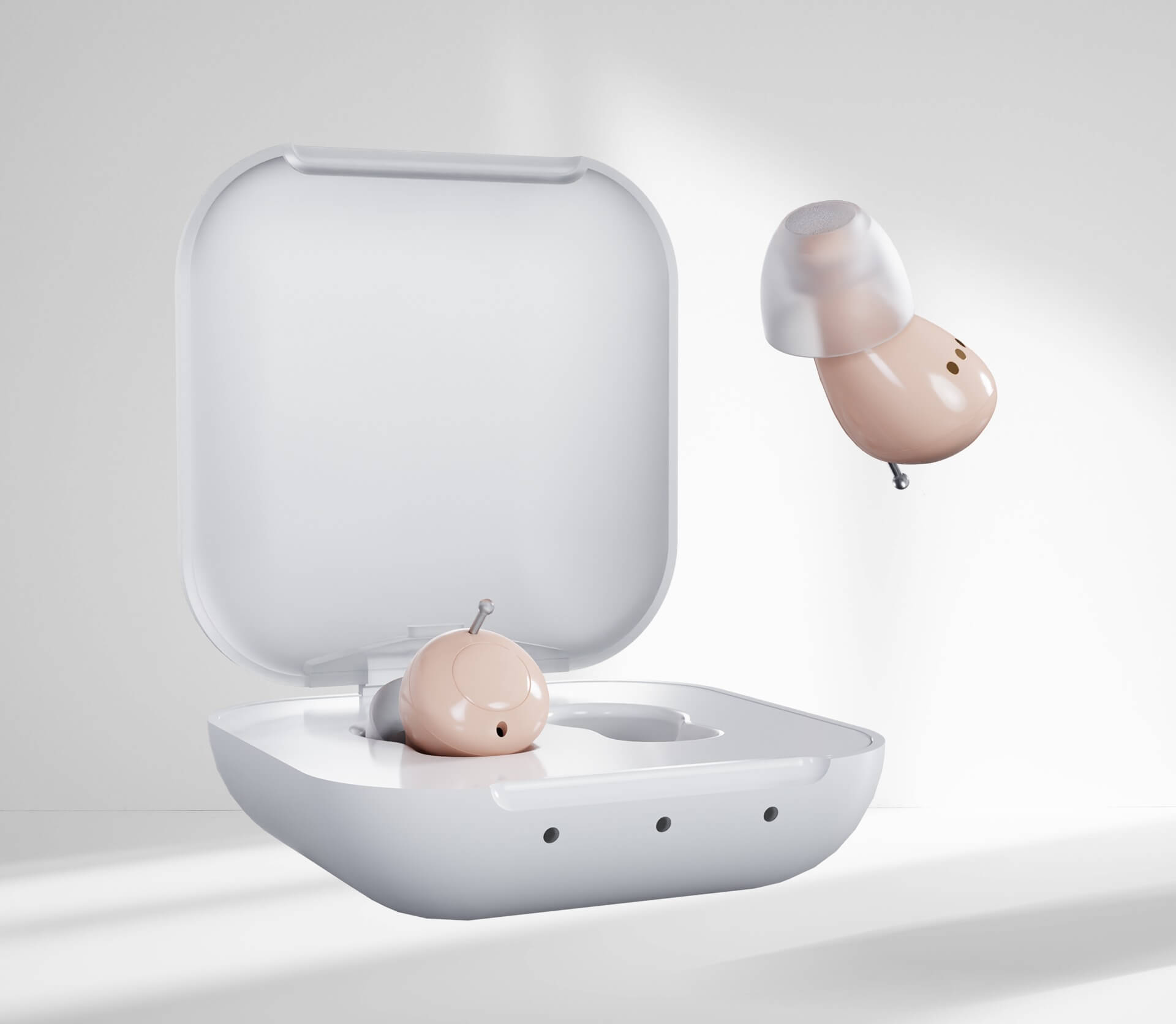
Wearable devices have emerged as a crucial component in the realm of assistive tech for dementia patients, offering innovative solutions to enhance both safety and security. These technologies are designed to support patients while allowing them to maintain a level of independence, thus empowering them to engage with their environments. Among the most significant advancements in this field are GPS trackers and health monitors, which provide invaluable peace of mind for caregivers and family members.
One of the defining features of wearable devices is their ability to incorporate geolocation services. These services enable caregivers to track the location of dementia patients in real-time, thereby reducing the risks associated with wandering, a common concern among individuals living with this condition. For instance, if a patient strays too far from a designated area, caregivers can receive alerts, ensuring a swift response to guide the individual back to safety.
Moreover, fall detection technology is another critical feature found in many wearable devices for dementia patients. This technology utilizes accelerometers and gyroscopes to monitor the user’s movements continuously. In the event of a significant fall, the device can automatically send alerts to designated caregivers, prompting immediate assistance. This proactive approach not only enhances patient safety but also minimizes the potential for serious injuries, which are often exacerbated by delayed response times.
Additionally, many wearable devices come equipped with emergency alert systems. By pressing a button on the device, patients can alert caregivers or family members in case of an emergency, ensuring they receive timely assistance. These features represent just a fraction of the myriad ways assistive tech for dementia patients can facilitate a safer living environment, affording patients the freedom to explore while enabling caregivers to monitor their well-being effectively.
Memory Aids: Tools for Daily Living
Assistive tech for dementia patients has made significant strides in enhancing the quality of life for those experiencing cognitive decline. Memory aids have emerged as vital tools that help individuals navigate daily tasks and appointments, thereby promoting independence and reducing stress. These aids take various forms, including digital reminders, calendars, and smartphone applications designed specifically for the needs of dementia patients.
Digital reminders can be customized to send alerts at specific times, ensuring that patients remember crucial activities such as taking medication or attending appointments. These notifications can be easily set up through smartphones or tablets, which many individuals are already familiar with. User-friendly designs that feature large text, contrasting colors, and simple interfaces make these applications accessible for those who may struggle with complex technology. In addition, some memory aids incorporate visual cues and audio prompts to further assist patients in remembering their tasks.
Calendars, both physical and digital, serve as effective memory tools for dementia patients. Families can create a visual calendar that outlines daily activities or significant events, enabling patients to recognize and anticipate upcoming responsibilities. Digital calendars can also be synchronized across devices, providing real-time updates for caregivers and family members, ensuring that everyone is informed about the patient’s schedule. Furthermore, some applications include built-in sharing features, allowing caregivers to add or modify events remotely, which enhances the communication between family members and caregivers.
By utilizing these memory aids, dementia patients can experience an improved ability to remember essential information, fostering a sense of control over their lives. The development of assistive technology in this area reflects a growing awareness of the unique challenges faced by those with cognitive impairments and highlights the importance of creating supportive environments that cater to their specific needs.
Smart Home Technologies: Creating a Supportive Environment
The advent of smart home technologies has significantly transformed the living conditions of dementia patients, offering a range of devices specifically designed to cater to their unique needs. These technologies aim to enhance the overall quality of life for individuals facing cognitive challenges by promoting independence while ensuring safety. In particular, smart lighting systems can be programmed to adjust automatically based on the time of day or the presence of an individual in a room. This feature is beneficial for dementia patients, who may struggle with orientation; soft lighting can guide them through their homes and mitigate the risk of falls.
Voice-activated assistants, such as Google Home and Amazon Alexa, represent another critical development in assistive tech for dementia patients. These devices can help individuals manage their daily routines by allowing them to set reminders for medications, appointments, or even daily activities without navigating complex interfaces. Furthermore, voice commands eliminate the need for physical interactions with devices, which can be challenging for some patients. Effective integration of these systems into daily life can significantly alleviate stress for both patients and their caregivers.
Moreover, smart security systems further contribute to a supportive environment, offering tools like door/window sensors and surveillance cameras. These systems can alert caregivers if a door has been left open or if an unauthorized exit has occurred, providing peace of mind for family members. The implementation of these technologies enables dementia patients to navigate their homes with greater autonomy, reducing feelings of anxiety and enhancing their independence. As smart home technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly vital role in creating accessible living environments tailored to the specific needs of dementia patients.
Communication Aids: Bridging the Gap
Effective communication is crucial for maintaining dignity and independence in dementia patients. Assistive tech for dementia patients includes a variety of communication aids designed to help these individuals express their needs, feelings, and thoughts. One prominent category of tools includes speech-generating devices, which allow users to communicate verbally through pre-recorded messages or text-to-speech functions. These devices can significantly alleviate frustration often experienced by patients who find it difficult to articulate themselves due to cognitive decline.
Additionally, communication apps tailored for dementia patients have emerged as invaluable resources. These apps often feature user-friendly interfaces that incorporate images, symbols, and prompts to facilitate conversation. By simplifying the communication process, such tools empower patients, enabling them to engage in meaningful interactions with family members and caregivers. Moreover, they can provide critical assistance in healthcare settings, where clear communication of symptoms or needs is vital for effective treatment and care.
Beyond mere functionality, the use of these assistive technologies can profoundly impact the emotional well-being of dementia patients. Enhanced interaction with loved ones fosters a sense of connection and belonging, which is essential for mental health. Regular communication helps mitigate feelings of isolation and frustration that many patients may experience as their condition progresses. By utilizing assistive tech designed specifically for dementia patients, caregivers can significantly improve their ability to support these individuals, making it easier to navigate daily challenges and maintain essential relationships.
Ultimately, the integration of communication aids in the care of dementia patients is a powerful tool that not only addresses practical communication barriers but also nurtures emotional connections, reinforcing the importance of maintaining relationships that enrich the lives of those affected.
Benefits of Assistive Technology for Caregivers
Assistive technology for dementia patients extends its advantages beyond the individuals living with the condition, significantly benefiting their caregivers as well. One of the most profound impacts of these technological solutions is the alleviation of the emotional and physical burdens associated with caregiving. With increased demands placed on caregivers, assistive technology can streamline daily routines, allowing for greater efficiency and reduced stress levels.
Tools such as medication reminders, digital checklists, and remote monitoring systems allow caregivers to manage numerous responsibilities simultaneously. This technological support enables caregivers to ensure that dementia patients receive timely medication and regular check-ins without constant oversight, leading to improved peace of mind. Furthermore, the time saved through these efficiencies opens opportunities for caregivers to engage in self-care and personal activities, which are crucial for their well-being.
In addition to time management, assistive tech enhances communication channels between caregivers and dementia patients. Devices designed to facilitate communication can help overcome barriers that arise due to cognitive decline. For instance, interactive digital tools can encourage conversations and assist in maintaining connections with family members. Caregivers often report a sense of fulfillment when they witness positive interactions made possible through such technology.
Moreover, many assistive technologies provide valuable insights into a patient’s behavior and health status. Wearable devices and home monitoring systems can track physical activity levels, sleep patterns, and even physiological markers, sending alerts to caregivers if intervention is needed. This level of monitoring allows caregivers to respond to health changes promptly, ensuring better support and care for dementia patients.
Overall, embracing assistive technology not only empowers dementia patients but also significantly enhances the experience for caregivers, leading to a more balanced and effective caregiving arrangement.
Challenges and Limitations of Assistive Technology
While assistive technology for dementia patients holds significant promise in enhancing the quality of life for these individuals, several challenges and limitations must be critically examined. One primary concern is device usability. Many assistive devices are designed with advanced technological features that may not be intuitive for older adults, particularly those with cognitive impairments. This complexity can lead to frustration and a reluctance to use the devices, undermining their potential benefits. To ensure the effectiveness of these tools, designers must prioritize user-friendly interfaces that cater specifically to the needs of dementia patients.
Cost also presents a substantial barrier to the widespread adoption of assistive technologies. Many families may find it financially challenging to invest in cutting-edge tools, especially when multiple devices are required to support various daily activities. Additionally, insurance coverage for these technologies is often limited, exacerbating financial constraints for caregivers. Therefore, addressing the affordability of assistive technology for dementia patients is crucial to making these resources accessible to a broader population.
Furthermore, the adoption of assistive tech among older adults can be hindered by their unfamiliarity with technology. Many seniors may feel intimidated by new devices and may be hesitant to engage with them, leading to low usage rates. This reluctance necessitates effective training for both patients and caregivers to overcome technological barriers. Comprehensive education programs are essential to familiarize users with the tools and to empower them to utilize assistive technology fully.
In conclusion, while assistive technology provides valuable support for dementia patients, addressing the challenges of usability, cost, and technology adoption is critical for maximizing its effectiveness. Recognizing and mitigating these limitations will contribute to enhancing the overall experience and outcomes for both patients and caregivers.
Future Trends in Assistive Technology for Dementia
The landscape of assistive technology for dementia patients is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in several key areas including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These innovations are being harnessed to enhance the quality of care and improve the experiences of both patients and caregivers. One of the most significant trends is the integration of AI into assistive devices, which allows for more personalized support tailored to the unique needs of each individual. This application of AI facilitates real-time monitoring and analysis of patient behavior, enabling timely interventions that can better address the complexities associated with dementia.
Machine learning algorithms are particularly noteworthy in this context, as they can learn from and adapt to the behaviors and changing conditions of dementia patients. As data is collected over time, these algorithms enable devices to anticipate the needs of users and provide customized reminders, alerts, or assistance. Such capabilities can significantly enhance the independence of patients, allowing them to engage more fully in daily activities while also reducing the stress for caregivers who may otherwise worry about their charges. The journey toward creating these responsive assistive technologies is indicative of a broader movement in healthcare toward individualized patient care.
Furthermore, the rise of telehealth services is expected to have a transformative impact on the field of dementia care. Through telehealth platforms, patients can receive timely consultations, manage medications, and participate in cognitive therapies from the comfort of their homes. This not only improves access to care but also fosters a sense of connection and support for those living with dementia and their families. As we look toward the future, these advancements in assistive technology will undoubtedly play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for dementia patients and supporting their caregivers. Such trends are worthy of observation and will shape the next generation of care solutions.